Microservice
In this lab, we will use example provided by DickyChesterwood. The docker images are available on Docker Hub
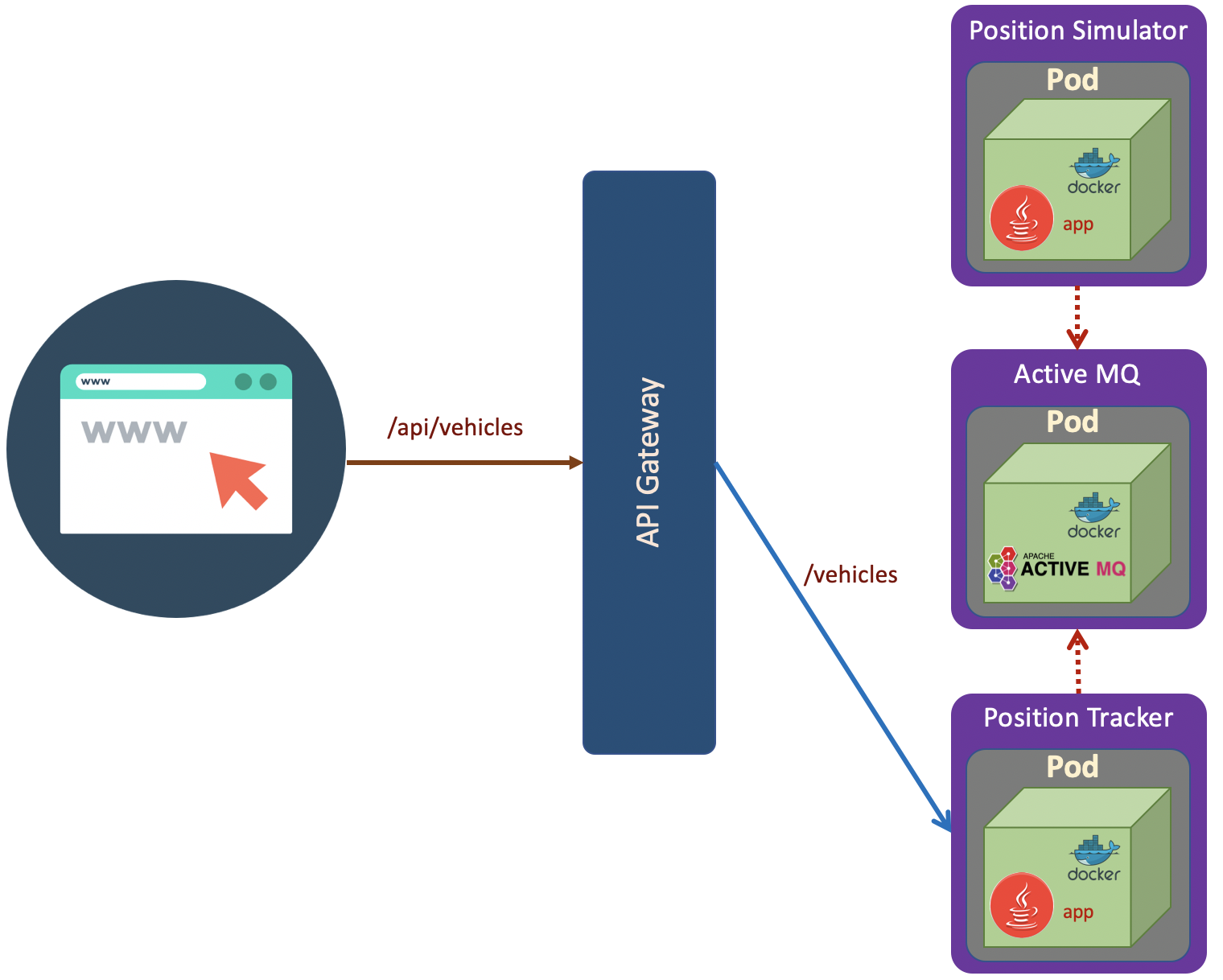 The scenario as shown in the above diagram. The deployment steps are:
The scenario as shown in the above diagram. The deployment steps are:
1. Queue (ActiveMQ)
First of all we will create active-mq.yaml
# ActiveMQ Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: queue
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: queue
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: queue
spec:
containers:
- name: queue
image: richardchesterwood/k8s-fleetman-queue:release1
---
# ActiveMQ Service
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: fleetman-queue
spec:
# This defines which pods are going to be represented by this Service
# The service becomes a network endpoint for either other services
# or maybe external users to connect to (eg browser)
selector:
app: queue
ports:
- name: http
port: 8161
nodePort: 30010
- name: endpoint
port: 61616
type: NodePort
kubectl apply -f active-mq.yaml
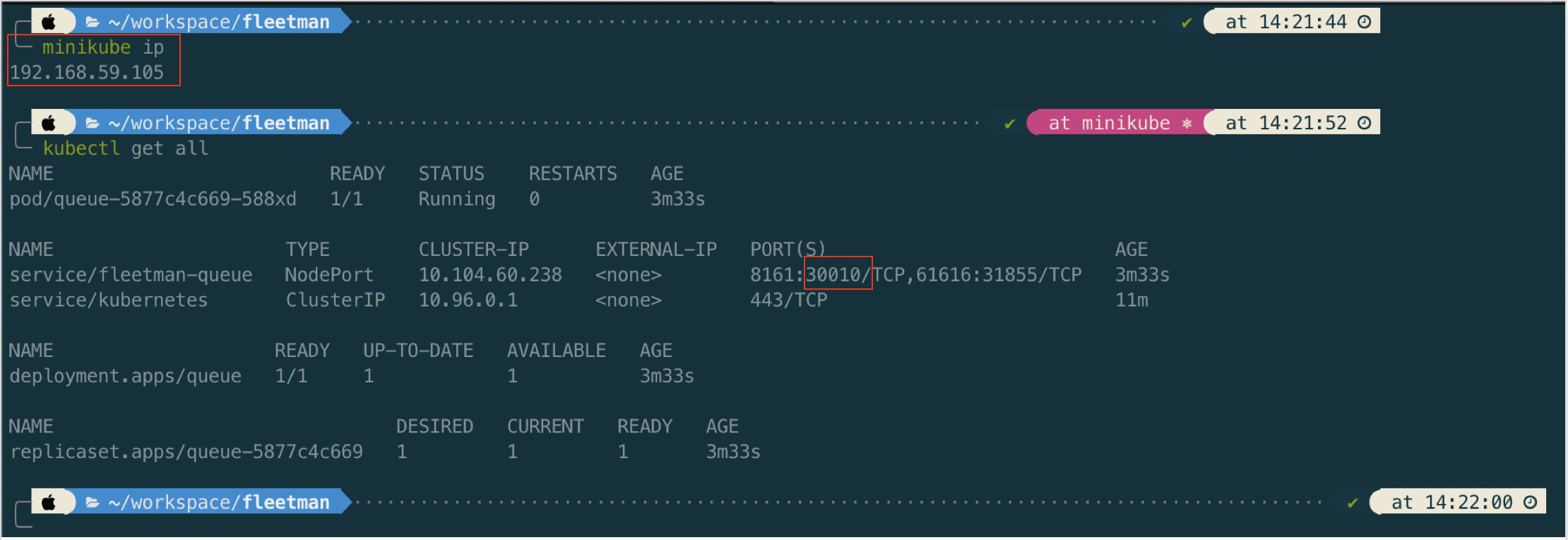
Now open in browser http://192.168.59.105:30010/
ActiveMQ default username/password is
admin/admin
2. Position Tracker
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: position-tracker
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: position-tracker
replicas: 1
template: # template for the pods
metadata:
labels:
app: position-tracker
spec:
containers:
- name: position-tracker
image: richardchesterwood/k8s-fleetman-position-tracker:release1
env:
- name: SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE
value: production-microservice
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: fleetman-position-tracker
spec:
# This defines which pods are going to be represented by this Service
# The service becomes a network endpoint for either other services
# or maybe external users to connect to (eg browser)
selector:
app: position-tracker
ports:
- name: http
port: 8080
nodePort: 30011
type: NodePort
![]()
When we hit through browser to http://192.168.59.105:30011/ we get 404 which means that the position tracker service (spring boot app) run well.
For checking purpose we can let the position tracker as
NodePort. For production purpose, we can consider to change theNodePorttoClusterIPsince position tracker microservice is not designed to be accessed from ouside cluster.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: position-tracker
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: position-tracker
replicas: 1
template: # template for the pods
metadata:
labels:
app: position-tracker
spec:
containers:
- name: position-tracker
image: richardchesterwood/k8s-fleetman-position-tracker:release1
env:
- name: SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE
value: production-microservice
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: fleetman-position-tracker
spec:
# This defines which pods are going to be represented by this Service
# The service becomes a network endpoint for either other services
# or maybe external users to connect to (eg browser)
selector:
app: position-tracker
ports:
- name: http
port: 8080
#nodePort: 30011
#type: NodePort
type: ClusterIP
3. Position Simulator
In the diagram, the position simulator is not designed to be accessed from outside the cluster. So it should be isolated and no port needed.
# Position Simulator Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: position-simulator
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: position-simulator
replicas: 1
template: # template for the pods
metadata:
labels:
app: position-simulator
spec:
containers:
- name: position-simulator
image: richardchesterwood/k8s-fleetman-position-simulator:release1
env:
- name: SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE
value: production-microservice
Save the above yaml as position-simulator.yaml and run apply command.
kubectl apply -f position-simulator.yaml
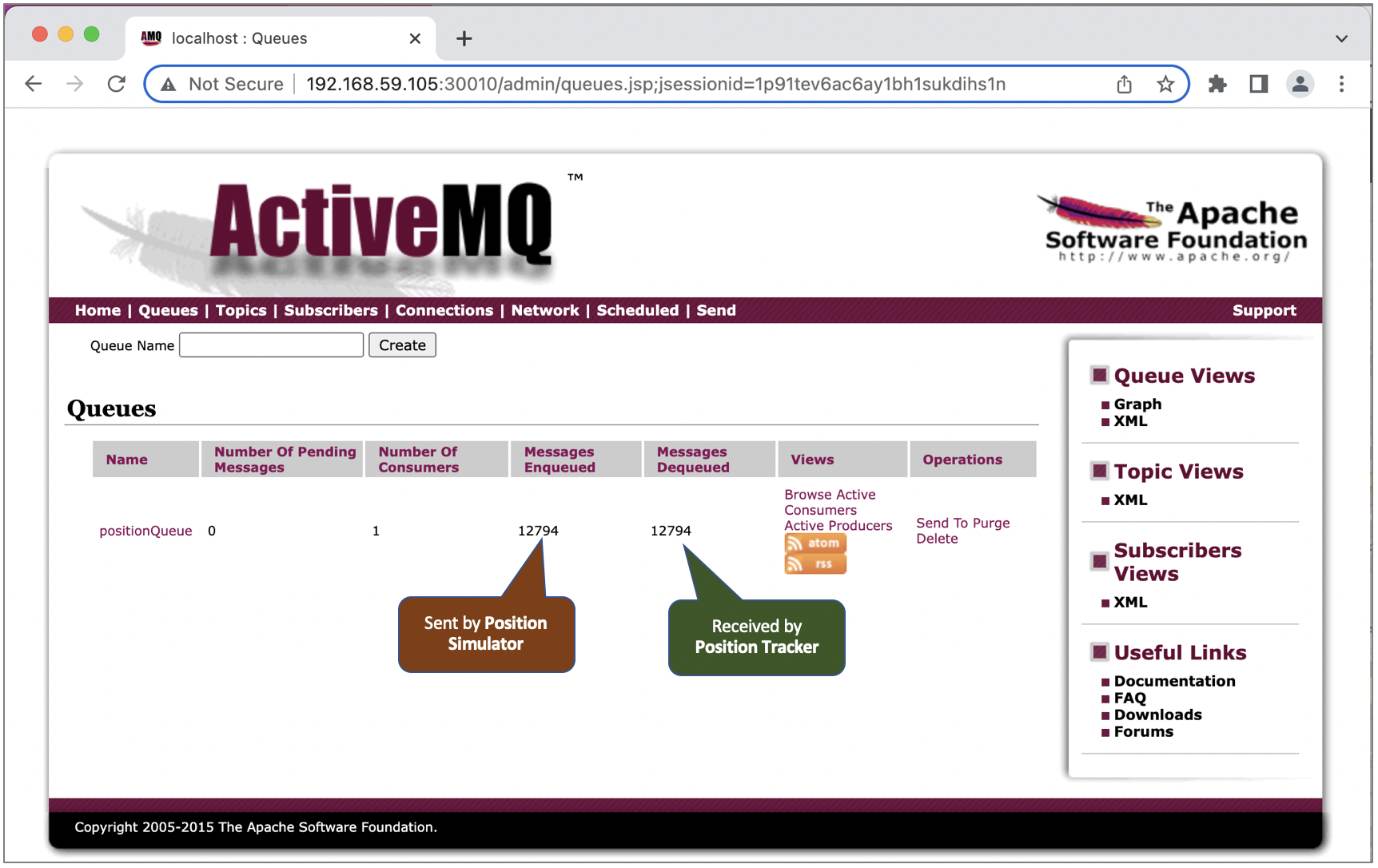
Once the position simulator running, we should see queue record in the ActiveMQ dashboard.
4. API Gateway
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api-gateway
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: api-gateway
replicas: 1
template: # template for the pods
metadata:
labels:
app: api-gateway
spec:
containers:
- name: api-gateway
image: richardchesterwood/k8s-fleetman-api-gateway:release1
env:
- name: SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE
value: production-microservice
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: fleetman-api-gateway
spec:
# This defines which pods are going to be represented by this Service
# The service becomes a network endpoint for either other services
# or maybe external users to connect to (eg browser)
selector:
app: api-gateway
ports:
- name: http
port: 8080
nodePort: 30020
type: NodePort
Let’s check the API gateway by open http://192.168.59.105:30020/ in browser.
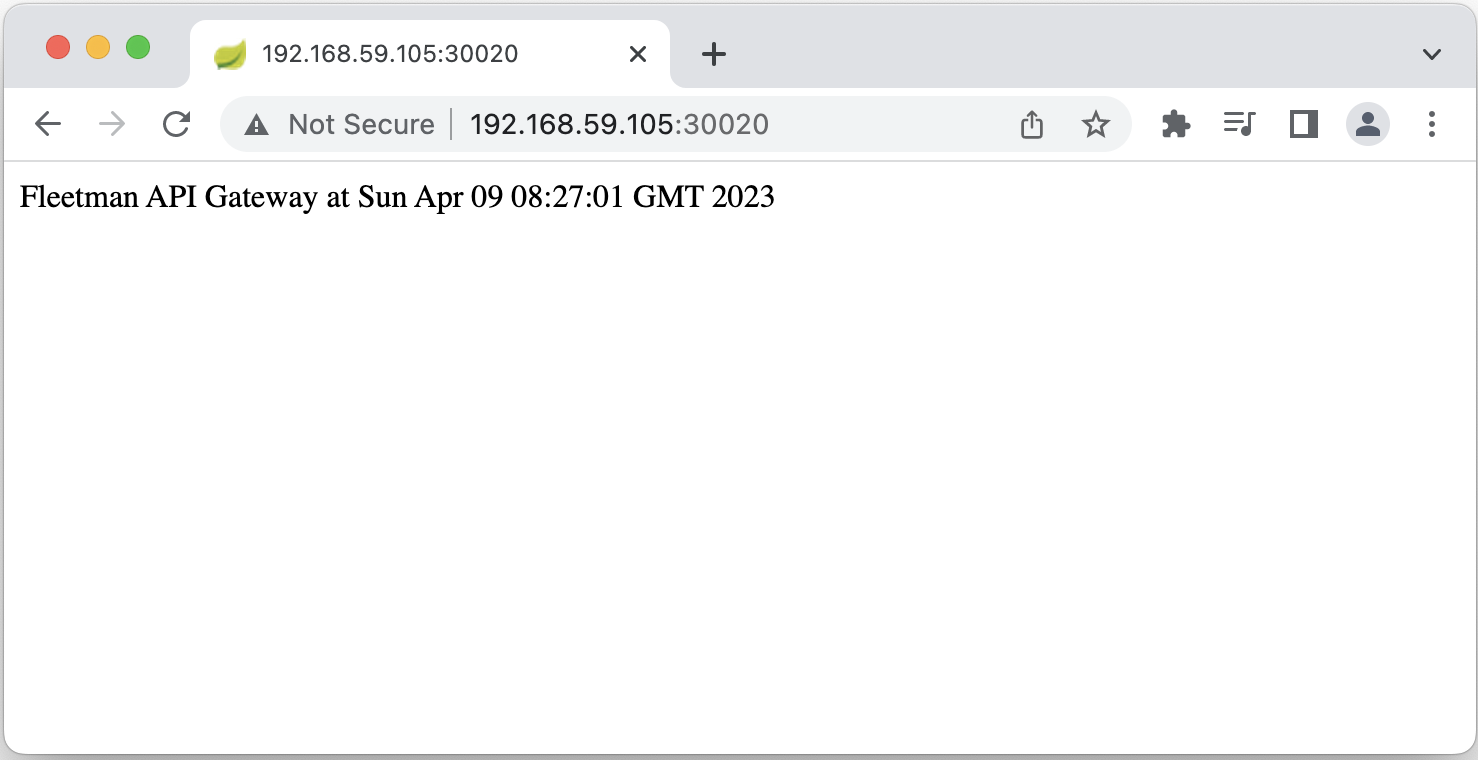
5. Webapp
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: webapp
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: webapp
replicas: 1
template: # template for the pods
metadata:
labels:
app: webapp
spec:
containers:
- name: webapp
image: richardchesterwood/k8s-fleetman-webapp-angular:release1
env:
- name: SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE
value: production-microservice
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: fleetman-webapp
spec:
# This defines which pods are going to be represented by this Service
# The service becomes a network endpoint for either other services
# or maybe external users to connect to (eg browser)
selector:
app: webapp
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
nodePort: 30080
type: NodePort
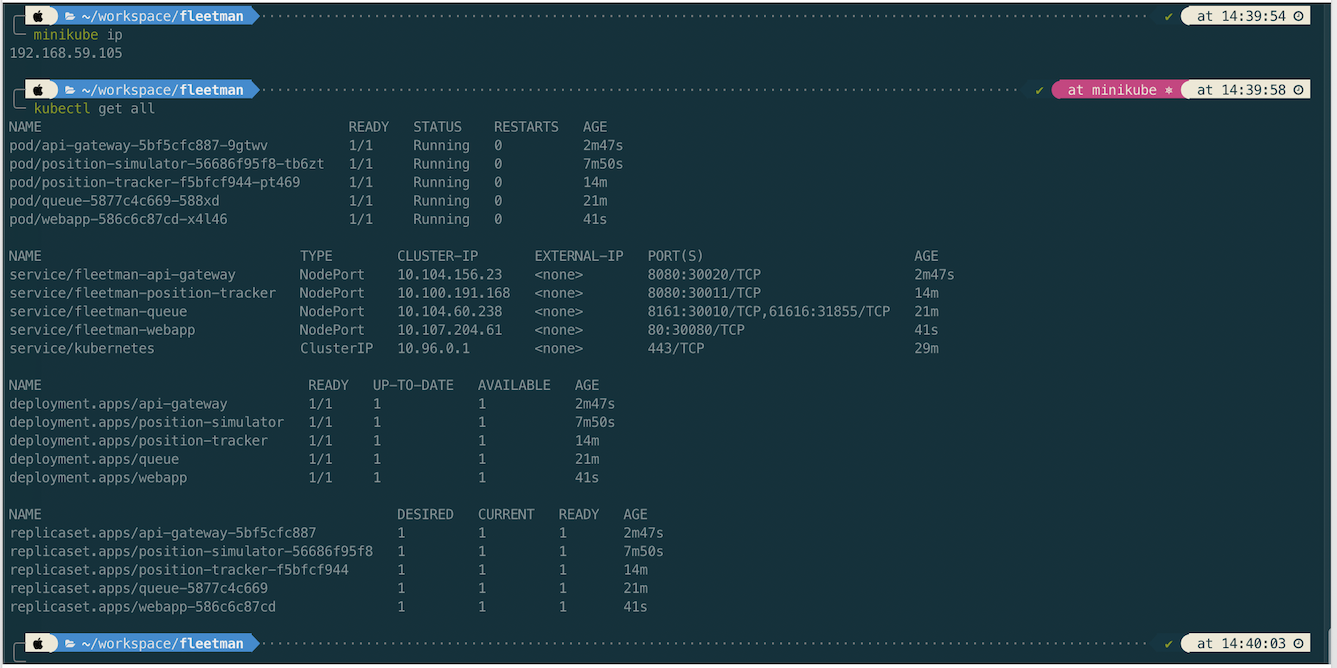
Let’s review all microservice deployments before we open the app.
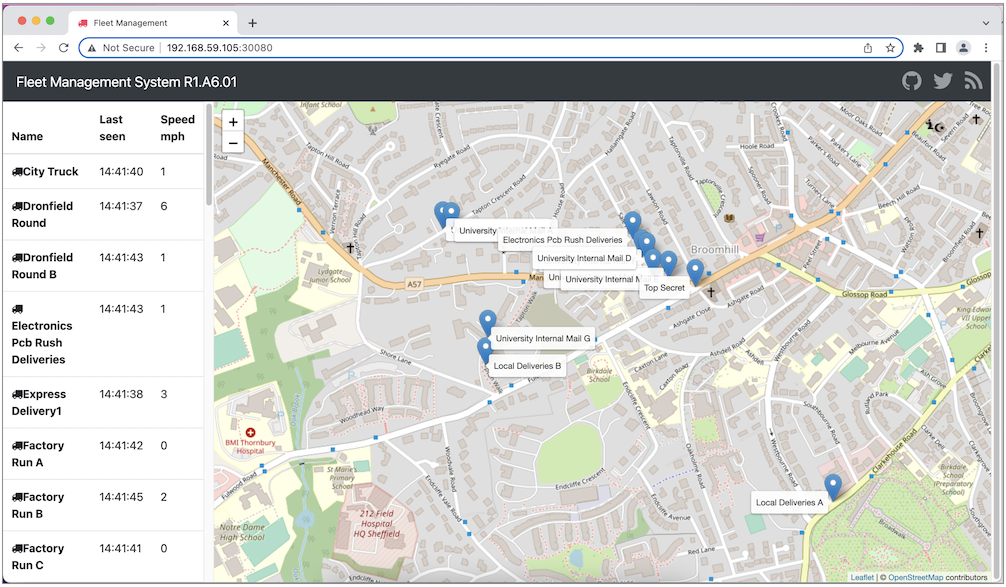
Lastly we can open the app in browser http://192.168.59.105:30080/
Investigating Kubernates Log
If we get an error on resource we can chek
# get pod description including kubernetes message while creating/updating the pod
kubectl describe pod position-simulator-56686f95f8-tb6zt
# get the application log (spring log)
kubectl logs api-gateway-5bf5cfc887-9gtwv
kubectl logs position-simulator-56686f95f8-tb6zt
# get the application log by following the log
kubectl logs -f position-simulator-56686f95f8-tb6zt
References
- https://github.com/DickChesterwood/k8s-fleetman/tree/release0-reconstruction-branch
- https://www.nginx.com/blog/microservices-at-netflix-architectural-best-practices/
