Creating a Service
a Service is a method for exposing a network application that is running as one or more Pods in your cluster. Different from Pod, Service is a long running object. A service has an IP address and has stable fixed port. We can attach a Service to a Pod.
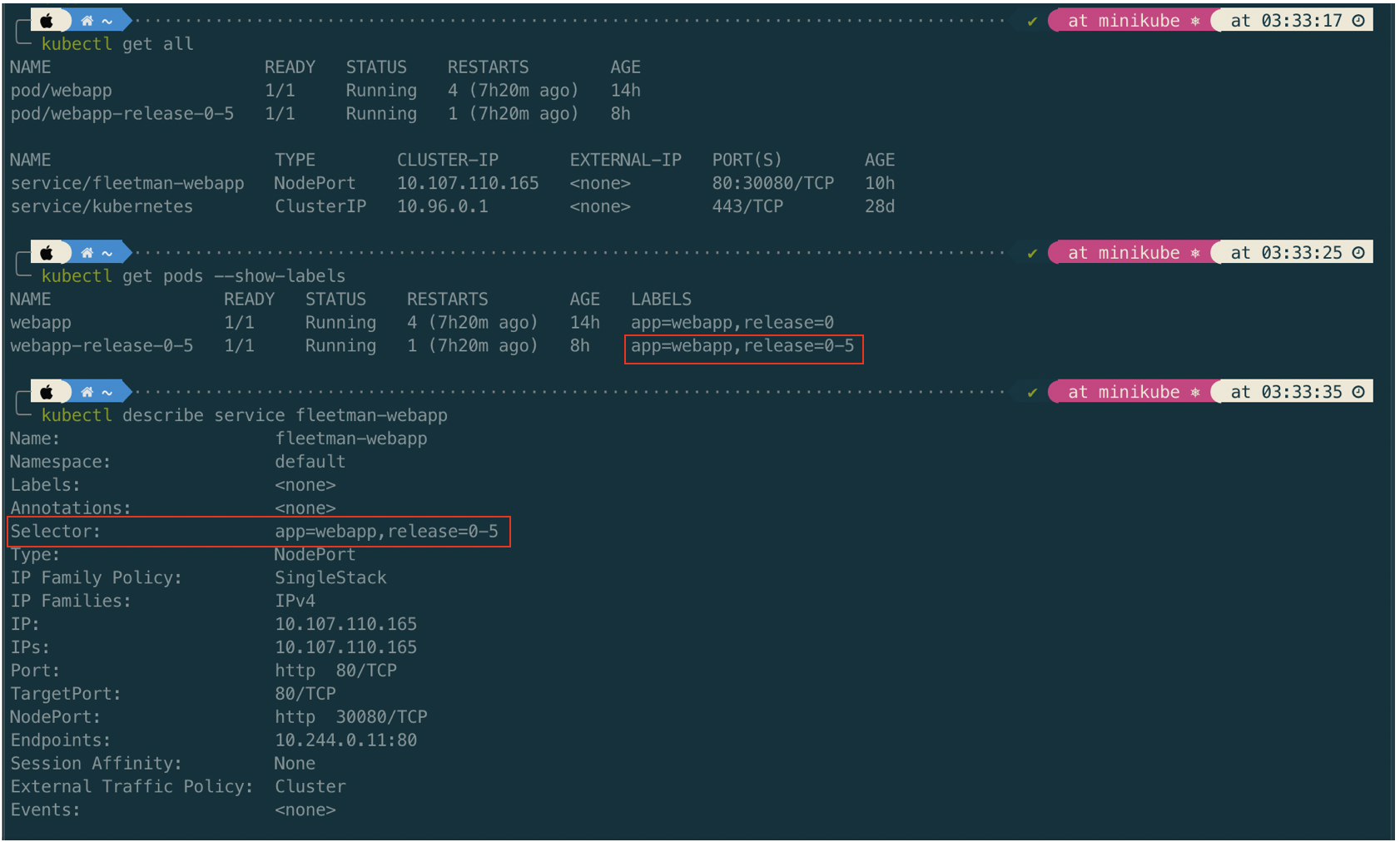
The Pod has a label which is a key value pair. The Service has a selector which is a key value pair to. The Service pointing to the Pod based on the match the key value pair on the selector and lable.
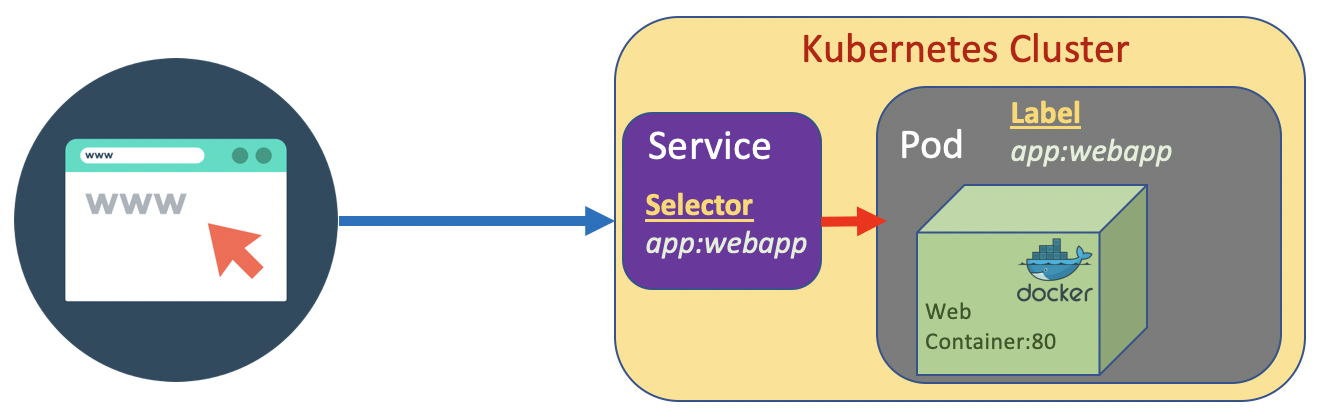
If a Service we create is designed to be access from internal cluster (such as microservice internal communication), we set the type to ClusterIP. On the other hand if we design it to be accessible from outside cluster, set the type to NodePort/.
The port that is allowed in Kubernetes cluster is greater than 30000
Let’s create a service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: fleetman-webapp
namespace: default
spec:
# This defines which pods are going to be represented by this service
# The service becomes a network endpoint for either other services
# or maybe external users to connect to (browser)
selector:
app: webapp # # can be any selector according to the label defined in pod ex: myapp:webapp
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
# the nodeport should be greater than 30000
nodePort: 30080
type: NodePort
kubectl apply -f service.yaml
Once the service created, check the status of serice and get ip of node (in this case we use minikube).
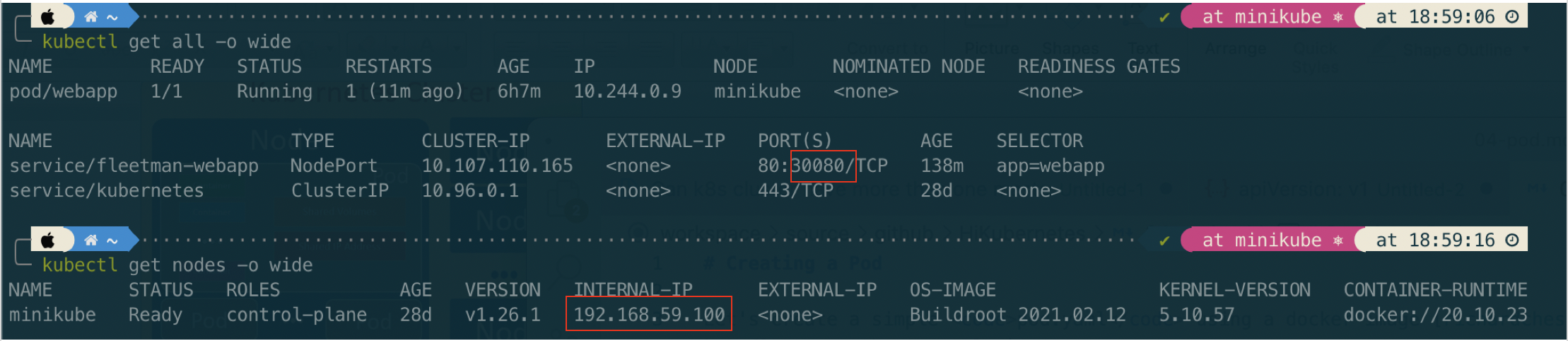
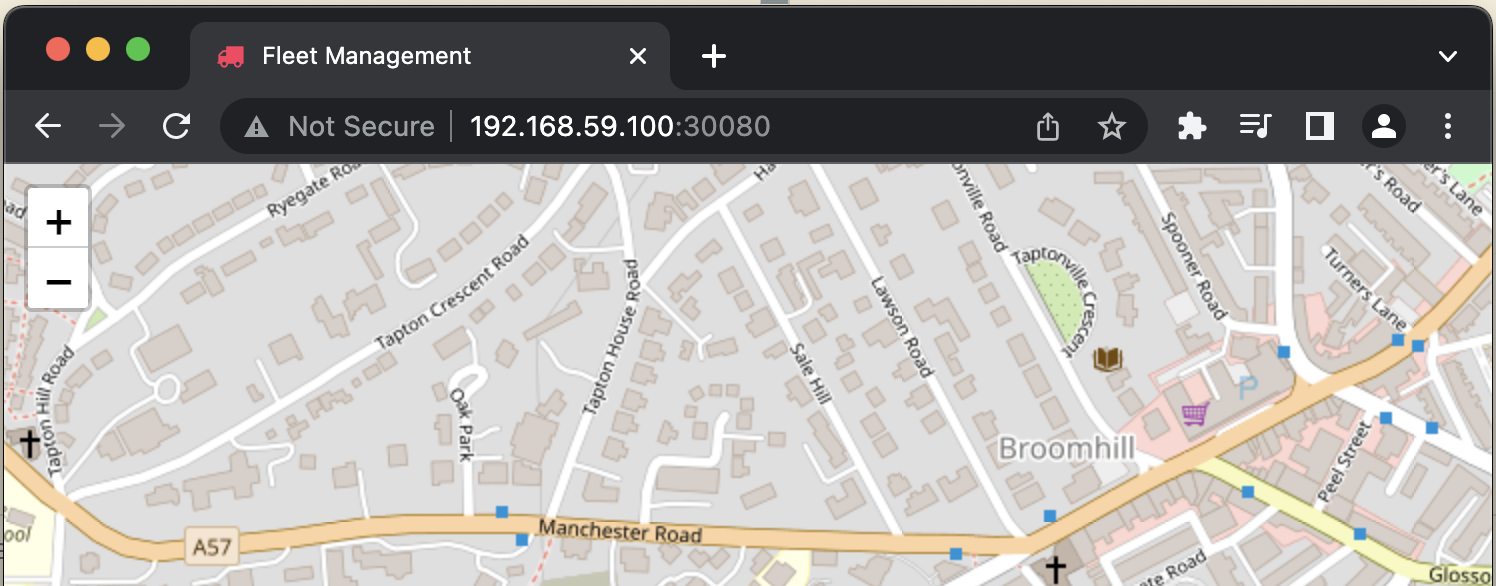
Then open browser: http://192.168.59.100:30080
Updating Version of App
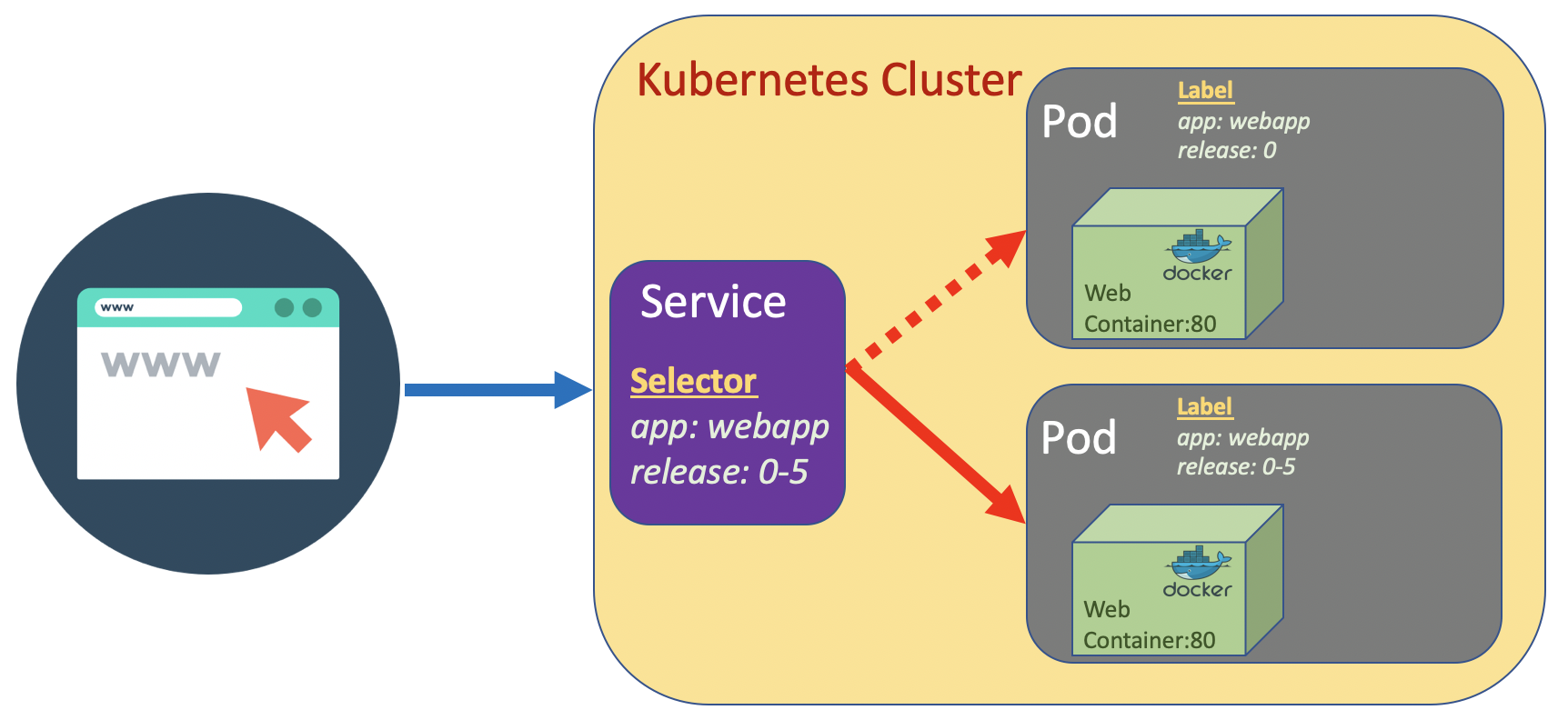
Let’s assume we want to update app to a new release, from richardchesterwood/k8s-fleetman-webapp-angular:release0 to richardchesterwood/k8s-fleetman-webapp-angular:release0-5
In this example we will add additional label called release and a new Pod named webapp-release-0-5 which represent a new release app.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: webapp
labels:
app: webapp # can be any label ex, myapp: webapp
release: "0" # should be a string
spec:
containers:
- name: webapp
image: richardchesterwood/k8s-fleetman-webapp-angular:release0
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: webapp-release-0-5
labels:
app: webapp # can be any label ex, myapp: webapp
release: "0-5" # should be a string
spec:
containers:
- name: webapp
image: richardchesterwood/k8s-fleetman-webapp-angular:release0-5
For service, we also add additional selector
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: fleetman-webapp
namespace: default
spec:
# This defines which pods are going to be represented by this service
# The service becomes a network endpoint for either other services
# or maybe external users to connect to (browser)
selector:
app: webapp # # can be any selector according to the label defined in pod ex: myapp:webapp
release: "0" # if we change this to "0-5" the service will point to app version 0-5. It is very fast without downtime.
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
# the nodeport should be greater than 30000
nodePort: 30080
type: NodePort
Let’s apply the pod.yaml and service.yaml
kubectl apply -f pod.yaml
kubectl apply -f service.yaml
Once the second Pod webapp-release-0-5 up, we can change the release value from "0" to "0-5" in the service. The changes in release in Service will pointing it to app version 0-5. It is very fast without downtime.
We can check further in the detail service information
Tips
We can search/list Pod by filtering on the command
kubectl get pod --show-labels -l release=0-5
If we refresh/force reload browser (http://192.168.59.100:30080), it will load the new release of app (version 0-5).
Service Port, TargetPort, and NodePort
There are several different port configurations for Kubernetes services:
-
Port
The port of this service -
TargetPort
The target port on the pod(s) to forward traffic to -
NodePort
The port on the node where external traffic will come in on.
Beside may have the 3 kind of ports, Kubernates service may have multiple port as well. Here is an example of service which has multiple port.
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: my-service
spec:
selector:
app: MyApp
ports:
# From inside the cluster, if you hit the my-service:8089 the traffic is routed to 8080 of the container(targetPort)
# From outside the cluster, if you hit host_ip:30475 the traffic is routed to 8080 of the container(targetPort)
- name: http
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8080
port: 8089
nodePort: 30475
- name: metrics
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 5555
port: 5555
nodePort: 31261
# From inside the cluster, if you hit my-service:8443 then it is redirected to 8085 of the container(targetPort)
# From outside the cluster, if you hit host_ip:30013 then it is redirected to 8085 of the container(targetPort)
- name: health
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8085
port: 8443
nodePort: 30013
